As a special commodity, the consumption of cosmetics is different from ordinary commodities. It has a strong brand effect. Consumers pay more attention to the image of cosmetics manufacturers and the quality of cosmetics products. Specifically, the quality characteristics of cosmetics are inseparable from the safety of the product (to ensure the safety of long-term use), stability (to ensure long-term stability), and usefulness (to help maintain the normal physiological functions of the skin and the radiant effect) and usability (comfortable to use, enjoyable to use), and even consumer preference. Among them, the most important safety and stability must be guaranteed through the theories and methods of microbiology and biochemistry.
Inspection rules for cosmetics
1.basic terminology
(1) Routine inspection items. Refers to the items that must be inspected for each batch of products, including physical and chemical indicators, sensory indicators, total number of bacteria in hygienic indicators, weight indicators and appearance requirements.
(2) Unconventional inspection items. Refers to items that are not inspected batch by batch, such as items other than the total number of bacteria in the hygiene indicators.
(3) Handle appropriately. Refers to the selection process of removing individual substandard products from the entire batch of cosmetics without damaging the sales packaging.
(4) Sample. Refers to the entire sample size of each batch.
(5) Unit product. Refers to a single piece of cosmetics, with bottles, sticks, bags and boxes as piece counting units.

2.Inspection classification
(1) Delivery inspection
Before products leave the factory, the inspection department of the manufacturer will inspect them batch by batch according to product standards. Only products that meet the standards can be shipped out. Each batch of products shipped out should be accompanied by a certificate of conformity. The consignee can divide the delivery batch into batches and conduct inspection according to the standard regulations. The delivery inspection items are routine inspection items.
(2)Type inspection
Normally, no less than once a year. Type inspection should also be carried out under any of the following circumstances.
1) When there are major changes in raw materials, processes, and formulas that may affect product performance.
2) When the product resumes production after a long-term suspension (more than 6 months).
3) When the factory inspection results are significantly different from the last type inspection.
4) When the national quality supervision agency proposes type inspection requirements.
Type inspection items include routine inspection items and non-routine inspection items.
3.Sampling
Products with the same process conditions, varieties, and production dates are considered to be one batch. The consignee can also deliver the products in one batch.
(1) Delivery inspection sampling
The sampling of packaging appearance inspection items shall be carried out according to the secondary sampling plan of GB/T 2828.1-2003. Among them, the unqualified (defect) classification classification inspection level (II) and qualified quality level (AQL: 2.5/10.0) are specified in Table 8-1.
Items that are destructive tests are sampled according to the GB/T 2828.1-2003 secondary sampling plan, where IL=S-3 and AQL=4.0.
The contents of packaging appearance inspection items are specified in the table.
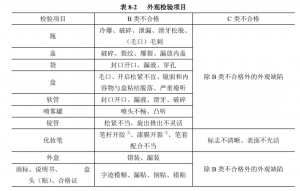
Note: ① This project is a destructive test.
Sampling for inspection of sensory, physical and chemical indicators and hygienic indicators. Corresponding samples are randomly selected according to the inspection items for inspection of various sensory, physical and chemical indicators and hygienic indicators.
For quality (capacity) index inspection, randomly select 10 unit samples and weigh the average value according to the corresponding product standard test method.
(2) Type inspection sampling
The routine inspection items in type inspection are based on the delivery inspection results, and sampling will not be repeated.
For unconventional inspection items of type inspection, 2 to 3 units of samples can be taken from any batch of products and inspected according to the methods specified in product standards.

4.Decision rules
(1)Delivery inspection and determination rules
When the hygiene indicators do not meet the corresponding standards, the batch of products will be judged as unqualified and shall not leave the factory.
When any of the sensory, physical and chemical indicators does not meet the corresponding product standards, the item indicators are allowed to be re-inspected, and the supply and demand parties jointly take samples. If they are still unqualified, the batch of products will be judged as unqualified and shall not leave the factory.
When the quality (capacity) index does not meet the corresponding product standards, double re-inspection is allowed. If it still fails, the batch of products will be judged as a failed batch.
(2)Type inspection judgment rules
The judgment rules for routine inspection items in type inspection are the same as those for delivery inspection.
If one of the non-routine inspection items in type inspection does not meet the product standards, the entire batch of products will be judged to be unqualified.
(3)Arbitration inspection
When a dispute arises between the supply and demand parties over product quality, both parties shall jointly conduct sampling inspections in accordance with this standard, or entrust a superior quality supervision station to conduct arbitration inspections.
5.transfer rules
(1)Unless otherwise specified, normal inspection shall be used at the beginning of the inspection.
(2)From normal inspection to stricter inspection. During normal inspection, if 2 batches out of 5 consecutive batches fail the initial inspection (excluding batches submitted for inspection again), the next batch will be transferred to stricter inspection.
(3) From tightened inspection to normal inspection. When strict inspection is carried out, if 5 consecutive batches pass the initial inspection (excluding re-submission of inspection batches), the inspection of the next batch will be transferred to normal inspection.
6.Check stop and resume
After the tightened inspection begins, if the number of unqualified batches (excluding batches submitted for inspection again) accumulates to 5 batches, product delivery inspection will be temporarily suspended.
After the inspection is suspended, if the manufacturer does take measures to make the batches submitted for inspection meet or exceed the standard requirements, the inspection can be resumed with the consent of the competent authority. It usually starts with stricter inspections.
7.Disposal after inspection
For quality (capacity) unqualified batches and Category B unqualified batches, the manufacturer is allowed to submit them for inspection again after appropriate treatment. Submit again for inspection according to the tightened sampling plan.
For Category C unqualified batches, the manufacturer will submit them for inspection again after appropriate treatment, and they will be inspected according to a strict sampling plan or handled through negotiation between the supply and demand parties.

Cosmetic Stability Test Method
Heat resistance test is an important stability test item for creams, lotions and liquid cosmetics, such as hair lotion, lipstick, moisturizing lotion, conditioner, hair dye lotion, shampoo, body wash, facial cleanser, hair mousse, Products such as creams and balms are required to undergo heat resistance tests.
Because the appearance of various cosmetics is different, the heat resistance requirements and test operation methods of various products are slightly different. However, the basic principles of the test are similar, that is: first adjust the electric constant temperature incubator to (40±1)°C, then take two samples, place one of them in the electric constant temperature incubator for 24 hours, take it out, and return to room temperature. Then compare it with another sample to observe whether it has thinning, discoloration, delamination and hardness changes to judge the heat resistance of the product.
2.Cold resistance test
Like the heat resistance test, the cold resistance test is also an important stability test item for creams, lotions and liquid products.
Similarly, because various types of cosmetics have different appearances, the cold resistance requirements and test operation methods of various products are slightly different. However, the basic principles of the test are similar, that is: first adjust the refrigerator to (-5 ~ -15) ℃ ± 1 ℃, then take two samples, place one of them in the refrigerator for 24 hours, take it out, and restore it. After room temperature, compare it with another sample to observe whether it has thinning, discoloration, delamination and hardness changes to judge the cold resistance of the product.
3.Centrifuge test
The centrifugal test is a test to test the shelf life of lotion cosmetics. It is a necessary test method to accelerate the separation test. For example, facial cleanser, moisturizing lotion, hair dye lotion, etc. all need to be centrifuged. The method is: place the sample in a centrifuge, test at a speed of (2000~4000) r/min for 30 minutes, and observe the separation and stratification of the product.
4.Color stability test
The color stability test is a test to check whether the color of colored cosmetics is stable. Since the composition and properties of various types of cosmetics are different, their inspection methods are also different. For example, the color stability test of hair lotion uses the ultraviolet irradiation method, and the color stability test of perfume and toilet water uses the drying oven heating method.
General inspection methods for cosmetics
1. Determination of pH value
The pH value of human skin is generally between 4.5 and 6.5, which is acidic. This is because the skin surface is divided into skin and sweat, which contains acidic substances such as lactic acid, free amino acids, uric acid, and fatty acids. According to the physiological characteristics of the skin, cream and lotion cosmetics should have different pH values to meet different needs. Therefore, pH value is an important performance indicator of cosmetics.
Weigh a portion of the sample (accurate to 0.1g), add 10 portions of distilled water several times, stir continuously, heat to 40°C to completely dissolve it, cool to (25±1)°C or room temperature, and set aside.
If it is a product with a high oil content, it can be heated to (70~80) ℃, and after cooling, remove the oil block for later use; powdery products can be precipitated and filtered for later use. Measure the pH value according to the instructions of the pH meter.
2. Determination of viscosity
When a fluid flows under the influence of external force, the resistance between its molecules is called viscosity (or viscosity). Viscosity is an important physical property of fluids and one of the important quality indicators for cream and lotion cosmetics. Viscosity is generally measured with a rotational viscometer.
Cashmere is fine cashmere that grows at the roots of goat's coarse hair. Since its diameter is thinner than sheep's wool, it can retain more still air, so it has good thermal insulation properties and is a magic weapon for goats to withstand the cold winter. And because the scales on the surface of cashmere fiber are thin and closely adhere to the fiber strands, cashmere products have better luster, smoother feel and less wrinkles than wool products. When goats shed their hair every spring, cashmere is obtained by artificial combing. It takes the hair of five goats to spin a 250g cashmere sweater. Due to the scarcity of output, cashmere is also known as "soft gold".

3. Measurement of turbidity
Perfume, head water and lotion products or some insoluble precipitates that have not been completely separated due to insufficient static aging time, or due to the insoluble matter in essence such as dipping gum and absolute wax content are too high, are easy to cause The product becomes cloudy, and cloudiness is one of the major quality issues with these cosmetics. Turbidity is mainly measured by visual inspection.
(1) Basic principles
Visually test the clarity of the sample in a water bath or other refrigerant.
(2) Reagents
Ice cubes or ice water (or other appropriate refrigerants 5°C lower than the measured temperature)
(3) Measurement steps
Put ice cubes or ice water in the beaker, or other appropriate refrigerants that are 5°C lower than the measured temperature.
Take two parts of the sample and pour them into two pre-dried φ2cm×13cm glass test tubes. The height of the sample is 1/3 of the length of the test tube. Plug the mouth of the test tube tightly with the stopper of a serial thermometer so that the mercury bulb of the thermometer is located in the middle of the sample.
Put another φ3cm × 15cm test tube on the outside of the test tube so that the test tube containing the sample is in the middle of the casing. Be careful not to make the bottoms of the two test tubes touch. Place the test tube in a beaker with refrigerant to cool down, so that the temperature of the sample gradually drops, and observe whether the sample is clear when it reaches the specified temperature. Use another sample as a control when observing. Repeat the measurement once and the two results should be consistent.
(4) Expression of results
At the specified temperature, if the sample is still as clear as the original sample, the test result of the sample is clear and not turbid.
(5) Precautions
① This method is suitable for the determination of turbidity of perfume, head water and lotion products.
②Different samples have different specified index temperatures. For example: perfume 5℃, toilet water 10℃.
4.Determination of relative density
Relative density refers to the ratio of the mass of a certain volume of material to the mass of the same volume of water. It is an important performance indicator of liquid cosmetics.
5.Determination of color stability
Color is an important performance indicator of cosmetics, and color stability is one of the main quality issues of cosmetics. The main method for measuring color stability is visual inspection.
(1) Basic principles
Compare the color change of the sample after heating to a certain temperature.
(2) Measurement steps
Take two portions of the sample and pour it into two φ2×13cm test tubes respectively. The height of the sample is about 2/3 of the tube length. Plug it with a cork and put one of them into a pre-adjusted temperature of (48±1)℃. In the constant temperature box, open the stopper after 1 hour, then keep it plugged, and continue to put it into the constant temperature box. After 24 hours, take it out and compare it with another sample. There should be no change in color.
(3) Result expression
At the specified temperature, if the sample still maintains its original color, the test result of the sample is that the color is stable and does not discolor.
6. Determination of essences in perfume and toilet water
Fragrance gives cosmetics a certain aroma and brings elegance and comfort to users. Almost all cosmetics use fragrance, so fragrance is one of the main base materials of cosmetics. The commonly used method for determination of fragrances in cosmetics is the ether extraction method.
(1) Basic principles
Utilizing the principle that essence is miscible in diethyl ether, the essence is extracted from the sample with diethyl ether, and the ether is removed and then weighed to obtain the essence content.
(2) Reagents
①Ether, anhydrous sodium sulfate
②Sodium chloride solution: Add an equal volume of distilled water to the saturated sodium chloride solution.
(3) Measurement steps
Accurately weigh (20~50) g of the sample to be tested (accurate to 0.000 2 g) into a 1 L pear-shaped separatory funnel, and then add 300 mL of sodium chloride solution. Then add 70 mL of diethyl ether, shake, and let stand to separate layers. Perform a total of three extractions. Place the three ethyl ether extracts together in a 1 L pear-shaped separatory funnel, add 200 mL of sodium chloride solution, shake and wash. , let stand for layering, discard the sodium chloride solution, transfer the ether extract to a 500 mL stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, add 5 g anhydrous sodium sulfate, shake, dry and dehydrate. Filter the solution into a dry and clean 300 mL beaker, rinse the Erlenmeyer flask with a small amount of ether, combine the eluent into the beaker, and place the beaker in a 50°C water bath for evaporation. When the solution evaporates to 20 mL, transfer the solution to a pre-weighed 50 mL beaker, continue evaporation until the ether is removed, place the beaker in a desiccator, vacuum and reduce the pressure to (6.67×10³) Pa, and place it for 1 h, weighing.

(4) Result calculation
The mass fraction w of the ether extract is calculated according to the following formula.
w=(m1-m0)/m
In the formula: m0——mass of beaker, g;
m1——The mass of the beaker and ether extract, g;
m——sample mass, g.
(5) Precautions
①This method is suitable for cosmetics such as perfume, cologne and toilet water.
②The allowable error of parallel test results is 0.5%.
Post time: Jan-17-2024





