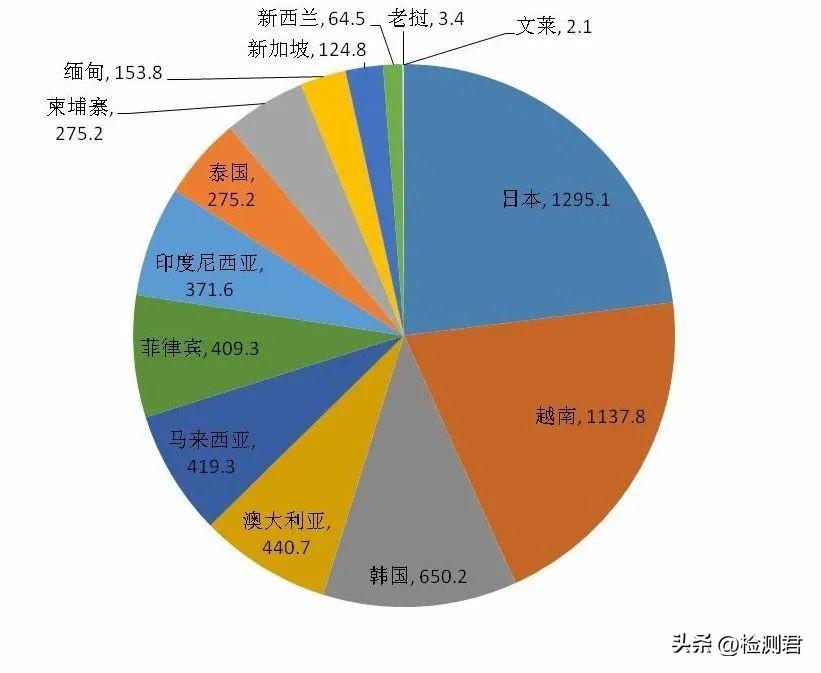
In January 2022, the regional comprehensive economic partnership agreement (RCEP) came into force, covering 10 ASEAN countries, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand. The 15 member countries cover nearly one-third of the world’s population, and their total exports account for about 30% of the global total. In 2021, China exported 562.31 billion yuan of textile and clothing to RCEP member countries, accounting for 27.6% of China’s total export value of textile and clothing. According to a single country, among the top ten export markets of China’s textile and clothing, RCEP member countries account for five, namely Japan, Vietnam, South Korea, Australia and Malaysia, with exports of 129.51 billion yuan, 113.78 billion yuan, 65.02 billion yuan, 44.07 billion yuan and 41.93 billion yuan respectively, accounting for 6.4%, 5.6%, 3.2%, 2.2% and 2.1% of the total export value of China’s textile and clothing.
Schematic diagram of China’s textile and clothing exports to RCEP member countries in 2021
In order to better implement the requirements of “paying more attention to and studying the technical trade measures of RCEP member countries” in the guiding opinions of the Ministry of Commerce and other six departments on the high-quality implementation of the regional comprehensive economic partnership agreement (RCEP), we are now collecting and sorting out the technical trade measures of RCEP textile and clothing, with a view to providing guidance for textile and clothing enterprises to develop the RCEP market.
Japan
01 regulatory authority
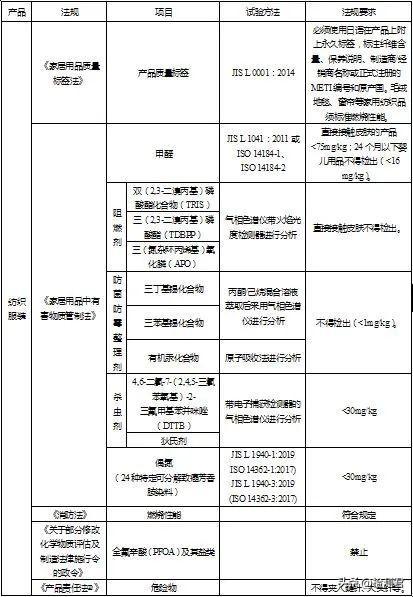
Japan’s textile and clothing import regulatory agencies mainly include the Ministry of health, labor and welfare (MHLW), the Ministry of economy, industry (METI), the consumer affairs agency (CAA) and the Japanese customs and Tariff Bureau. 02 technical regulations and standards
The general requirements for quality labels of textiles and clothing are specified in the household goods quality label law ① and the regulations on quality labels of textiles ②. For details, see JIS L 0001:2014 identification of washing and maintenance labels of textiles ③. The law on the control of hazardous substances in household articles ④ and its implementing regulations ⑤ regulate hazardous substances in textiles and clothing, and list the names, applicable products and test methods of hazardous substances. The outline of control standards for hazardous substances in household articles ⑥ supplements the limit requirements. The administrative decree on partial revision of the enforcement order on the evaluation and manufacture of chemical substances ⑦ stipulates that the import of textile and clothing containing perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and its salts is prohibited. Article 8-3 of the fire protection law ⑧ stipulates the burning performance and label requirements of certain textile and clothing. See the relevant materials ⑨ of the Japan Fire Protection Association for details. The product liability law ⑩ stipulates that the producer shall bear the responsibility for the death, injury or property damage caused by product defects (such as broken needles). In addition, the textile and clothing products using fur or leather also need to meet the requirements of the Washington Convention, the hunting act for wildlife protection, the Livestock Infectious Disease Control Act, and the endangered wildlife species protection act.
03 conformity assessment procedure
1. After the imported textile and clothing are tested by the designated agency to conform to the Japanese JIS industrial standards, the JIS mark can be affixed on the products, indicating that they have obtained the JIS certification of the Japan Industrial Standards Investigation Association. The following signs are used from left to right to indicate that the product complies with JIS product standards; Marks conforming to processing technical standards; A sign that complies with JIS standards that specify certain special aspects such as performance, safety, etc.
2. Textile and clothing can also be attached with voluntary qualification marks, such as SIF mark (certificate of high-quality products of Japan textile quality and Technology Center), silk mark (products certified by international silk textile association are made of 100% silk), hemp mark (certificate of high-quality products of Japan linen, ramie and jute Textile Manufacturers Association), SEK mark (products certified by Japan Textile Function Evaluation Association) and Q mark (certificate of high-quality products of Q mark Committee). 3. The Ministry of economy, trade and industry of Japan conducts market supervision through on-site spot inspection and public reporting, and will notify the manufacturer or supplier to rectify the textile and clothing that are unqualified or not labeled according to the above regulations. If the enterprise operator fails to rectify in time, the enterprise operator will be sentenced to fixed-term imprisonment of not more than one year and a fine of not more than 1 million yen in accordance with the provisions of the Japanese industrial standardization law.
04 warm tips
Enterprises exporting textile and clothing should pay attention to the supervision of harmful substances of household products in Japan, especially the items not specified in the mandatory standards of China’s textile and clothing, such as flame retardants, insecticides, fungicide and mold proof finishing agents, perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and its salts. Japan requires that the formaldehyde content of baby products under 24 months of age should be less than 16mg / kg, which is stricter than the provisions of GB 18401 (20mg / kg) in China. Attention should also be paid. In addition, Japan has strict requirements for broken needles, and imported clothing must pass the inspection of broken needles. It is suggested that enterprises use needle testing machines to strengthen the inspection.
Vietnam
01 regulatory authority
Vietnam’s textile and clothing safety standards are formulated by the General Administration of standards, metrology and quality (stameq) under the Ministry of science and technology, which is responsible for standardization, metrology, productivity and quality management. The Ministry of industry and trade is responsible for the safety supervision of textile and clothing. The science and technology department under the Ministry is responsible for reviewing and evaluating the business registration files of certification, evaluation and testing institutions, and the comprehensive market management department under the Ministry is responsible for organizing and guiding the market management divisions of provinces and municipalities directly under the central government to inspect, control and deal with violations of product and commodity quality regulations. Imported textiles and clothing shall be released by the customs.
02 technical regulations and standards
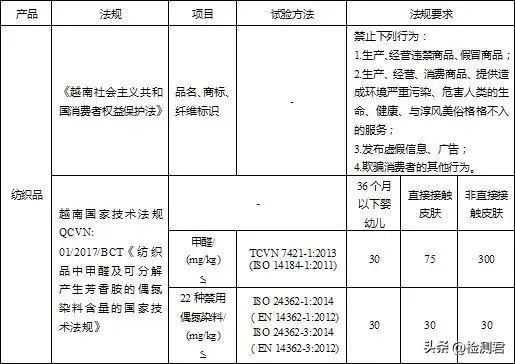
Vietnam’s textile and clothing technical regulations are qcvn: 01 / 2017 / BCT national technical regulations on the content of formaldehyde and azo dyes that can decompose into aromatic amines in textiles (regulations issued 21 / 2017 / tt-bct ⑪ and subsequent amendments 07 / 2018 / tt-bct ⑫ and 20 / 2018 / tt-bct ⑬). The commodity labeling regulations ⑭ specify the labeling requirements for commodities sold in Vietnam. The labels must be written in Vietnamese, including fiber composition, technical specifications, warning information, use and storage instructions, production year, etc.
03 conformity assessment procedure
1. The products and commodities sold in the Vietnamese market must comply with the provisions of qcvn: 01 / 2017 / BCT national technical regulations on the content of formaldehyde and azo dyes that can decompose into aromatic amines in textiles; In accordance with the Notice No. 28 / 2012 / tt-bkhcn ⑮ and Notice No. 02 / 2017 / tt-bkhcn ⑯ of the Ministry of science and technology, the conformity mark (CR mark) shall be printed. 2. Import and export customs clearance in Vietnam requires various documents specified in 38 / 2015 / tt-btc ⑰, 39 / 2018 / tt-btc ⑱, 60 / 2019 / tt-btc ⑲ and 06 / 2021 / tt-btc ⑳ dated January 22, 2021. In addition, due to the implementation of the new customs law, electronic customs clearance must be carried out in principle.
04 warm tips
The restrictions on harmful substances in textile and clothing in Vietnam are more relaxed than those in China. For example, the requirements for formaldehyde in articles for infants and young children under 36 months are not more than 30mg / kg (20mg / kg in China), and 22 azo substances are not more than 30mg / kg (24 azo substances are not more than 20mg / kg in China). Export to Vietnam shall focus on the requirements of qcvn: 01 / 2017 / BCT national technical regulations on the content of formaldehyde and azo dyes that can decompose into aromatic amines in textiles, such as the conformity mark and declaration of conformity.
Post time: Aug-22-2022