Plastic is synthetic resin, which is made of petroleum and has been praised as “one of the greatest inventions of mankind in the 20th century”. The wide application of this “great invention” has brought great convenience to people, but the disposal of waste plastics has become a thorny problem for all mankind. According to statistics, only 9% of the more than 10 billion tons of waste plastics produced globally since the 1950s can be recycled. Taking plastic packaging as an example, if no restrictions are imposed, the weight of plastic waste in the sea will exceed that of fish by 2050, calculated according to the current waste quantity. Plastic recycling economy is an important way to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality, and is also the core meaning of accelerating the green transformation of development mode, accelerating the construction of waste recycling system, and promoting ecological priority, saving and intensive, green and low-carbon development proposed in the report of the 20th CPC National Congress. This article takes you to understand the basic situation of waste plastic recycling at home and abroad.

The significance of accelerating the construction of waste plastic recycling system
Improve economic benefits
According to the conservative estimate of the United Nations Environment Programme, the environmental cost of the inefficient cycle of plastic packaging around the world is about $40 billion, and about 95% of the value of plastic packaging materials is wasted due to one-time use, which will cause direct economic losses of $80 billion to $120 billion annually.
2. Reduce white pollution
Plastic waste pollution not only pollutes the natural environment, but also harms human and animal health. The latest research shows that plastic particles are found in human blood vessels and placenta of pregnant women. According to the report released by the World Wide Fund for Nature in 2019, the average person worldwide consumes 5 grams of plastic per week, which is equivalent to the weight of a credit card.
3. Reduce carbon emission pollution
The carbon emission of the whole life cycle of 1 ton of waste plastics from production to final combustion is about 6.8 tons, the total carbon emission of each stage of the physical cycle of waste plastics is 2.9 tons, and the total carbon reduction of the physical cycle is about 3.9 tons; The total carbon emission of each link of the chemical cycle is 5.2 tons, and the carbon reduction is about 1.6 tons.
4. Saving oil resources
With the continuous progress of recycling technology, it is expected that the recycling rate of plastics will increase from 30% to more than 60% in 2060, saving 200 million tons of oil resources, which will have a profound impact on the pattern of the refining industry.
5. Improve enterprise competitiveness
The EU packaging tax and carbon border tax will be levied soon. It is estimated that the amount of plastic products levied in China will reach 70 billion yuan in 2030, while the profit of resin production enterprises in China is expected to be 96 billion yuan by 2030, and the tax intensity will reach 3/4. However, if enterprises add a certain proportion of recycled materials to plastic products, it will be possible to reduce or even exempt taxes, thus improving the competitiveness and brand influence of enterprises.

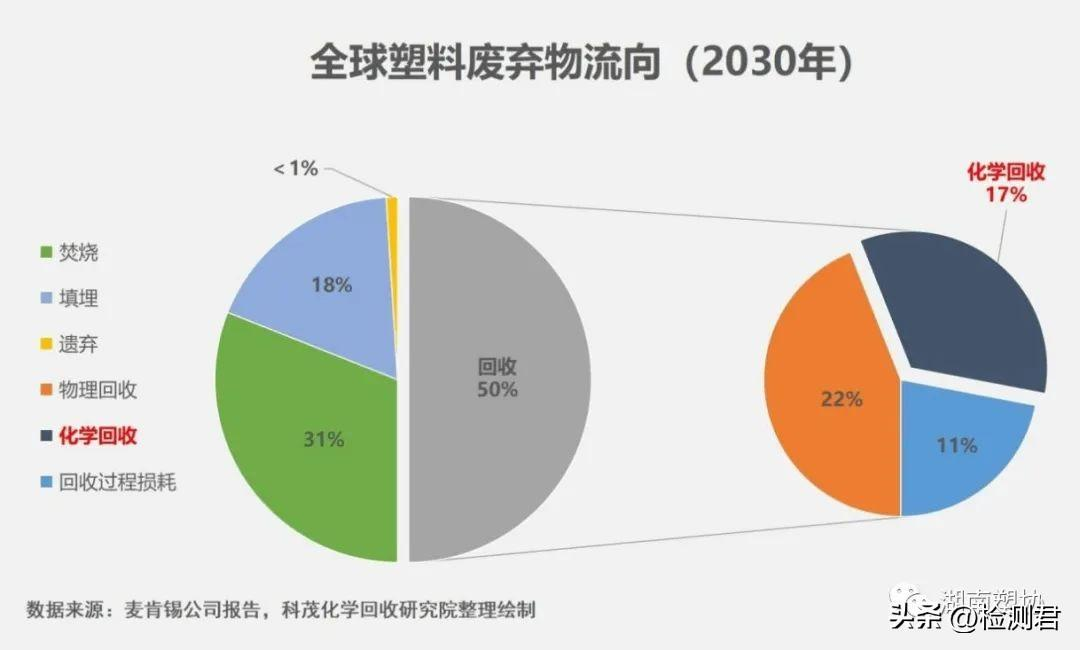
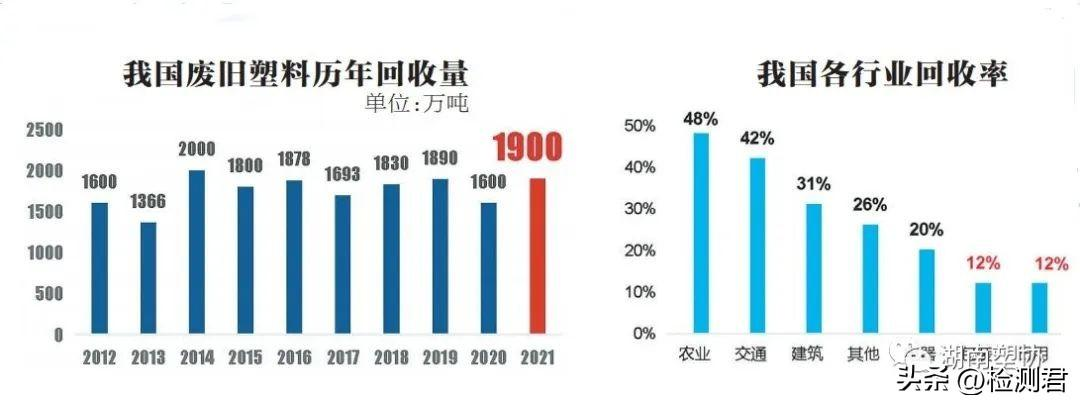
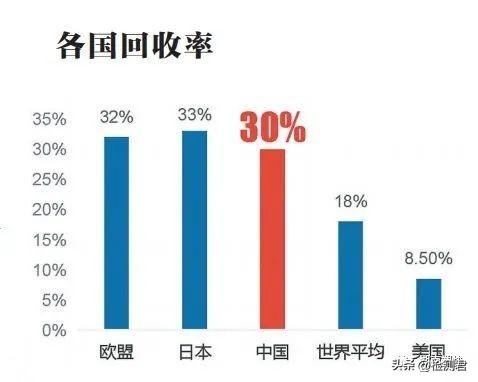
Recycling of waste plastics in China
China is the world’s largest plastic manufacturing, consumption and export country. In recent years, with the continuous improvement of people’s living standards, the output of waste plastics has also increased year by year. In 2021, plastics will account for 12% of China’s solid waste. At the same time, as people’s awareness of environmental protection has gradually increased, the proportion of plastic recycling has also increased steadily. According to the OECD 2020 report, it is expected that the recycling rate of waste plastics in the whole life cycle will increase from 8% in 2019 to 14% by 2060.
Many giants cluster in the field of chemical recycling of waste plastics
Nexus: It is planned to have at least 12 large factories in five years to recycle film waste from various sources by chemical means.
BASF: BASF invested 20 million euros in Quantafuel, a Norwegian company, to further develop and improve the process of using mixed plastic waste to produce pyrolysis oil.
SABIC: Multi-party cooperation aimed at increasing the production of certified cyclic polymers recovered from waste plastics and participating in the marine plastic chemical recovery project.
Total Energy: signed a long-term commercial agreement with Vanheede Environment Group to supply post-consumer recycling (PCR) raw materials
ExxonMobil: After the expansion of the plant in Texas, it will become one of the largest advanced plastic waste recycling facilities in North America.
Mura: The proprietary technology HydroPRS can avoid producing “carbon” and maximize the production of hydrocarbon products.
Dow: It is actively seeking to establish business partners with customers to expand the scale of chemical recovery technology as soon as possible.
Braskem (the largest polyolefin producer in the Americas): It is confirmed that the production of valuable intermediates such as aromatics and monomers is high.

Expert Viewpoint
Plastic cycle boosts green transformation of development mode
Fu Xiangsheng, Vice President of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation
Since its birth, plastics have made important contributions to the progress of human civilization, especially in replacing steel and wood, energy conservation and emission reduction. But now, it has become a global consensus to control plastic pollution. Plastic recycling economy is an important measure to reduce plastic environmental pollution.
Plastic recycling economy is divided into physical cycle and chemical cycle. Physical recycling is the practical path of recycling waste plastics in cascade. Chemical recycling can realize the high value reuse of waste plastics, and many enterprises at home and abroad have made important achievements.
Some use depolymerization or decomposition methods to reduce waste plastics to monomers and re-polymerize to realize chemical cycle. It is understood that the earliest DuPont and Huntsman in recent years have mastered the “methanol decomposition technology” to decompose waste polyester (PET) beverage bottles into methyl terephthalate and ethylene glycol monomers, and then re-synthesize new PET resin, realizing a closed-loop chemical cycle.
Others are gasification of waste plastics into syngas or pyrolysis into oil products, re-synthesis of chemicals and polymers. For example, BASF is developing a thermal cracking process that converts waste plastics into syngas or oil products, and uses this raw material to produce various chemicals or polymers in the Ludwigshafen integrated base, with the quality reaching food grade; Eastman realizes chemical recovery of a series of polyester plastic wastes through polyester regeneration technology, which can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 20%~30% compared with traditional processes; The project is planned to be put into operation in September 2023 by using the fluidized bed gasifier to gasify the waste plastic with low purity and not easy to recycle and produce methanol from the obtained syngas. This method can comprehensively reduce the carbon dioxide emissions by 100000 tons per 60000 tons of waste plastic. China Petrochemical Academy of Sciences, Aerospace Science and Industry and other enterprises have also achieved phased results in plastic recycling.
Chemical cycle is not a difficult problem from a technical point of view, because most chemical reactions are reversible: they can be decomposed if they can be synthesized, and they can be depolymerized if they can be polymerized. At present, the biggest obstacle is economic. It is cost and price. Therefore, technical solutions alone are not enough, but also need policy promotion, as well as people’s consensus and global action.
Accelerate the application and popularization of chemical recovery technology
Li Mingfeng, President of Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum and Chemical Technology
Chemical recycling of waste plastics is recognized as a low-carbon, clean and sustainable recycling method at home and abroad. In recent years, international chemical giants have accelerated their layout in the field of plastic recycling. LG, Saudi Basic Industry Corporation, BP and other internationally renowned enterprises have carried out research on the recycling of plastics. Among them, chemical recovery is the most important. Because chemical recovery is applicable to mixed waste plastics with high impurity content and cannot be physically recovered, it is considered as the future technical development direction by the industry. At present, only 12% of waste plastics in China are recycled by physical methods, and there is almost no chemical method, so there is still huge room for development.
The promotion of chemical recovery is bound to be supported by technology. Waste plastic pyrolysis technology is the key core technology that almost all enterprises will use. However, the development of waste plastics pyrolysis technology is very difficult, because there are more than 200 kinds of plastic raw materials involved, including general plastics, special plastics and engineering plastics, which makes the technical requirements of various refining and chemical enterprises very complex. At present, although the chemical recovery technology of waste plastics in China has achieved rapid development, it is still in the stage of expanding from small-scale to pilot or industrial demonstration. The rapid realization of technological breakthroughs requires greater technological research and development and broader cooperation.
In 2021, led by the Academy of Petroleum Sciences, 11 units, including the Joint Engineering Construction Company, Yanshan Petrochemical, Yangzi Petrochemical, Maoming Petrochemical, China Academy of Environmental Sciences, Beijing Institute of Petroleum and Chemical Technology, Tongji University, Zhejiang Yangtze River Delta Institute of Circular Economy and Technology, applied for the “Industrial Technology Innovation Center for Chemical Recycling of Waste Plastics” of the Petrochemical Federation and successfully won the license. In the next step, CAS will rely on the center to carry out industry-university-research collaborative innovation, strive to create a research and development platform for high-value utilization technology of waste plastics suitable for different types of plastics and different sources, develop waste plastics directional conversion technology, carry out the development and industrial application research of new waste plastics chemical recovery process and different technology combination processes, and make the waste plastics chemical recycling technology reach the international leading level.
Make waste plastic recyclable
Guo Zifang, Vice President of Sinopec Beijing Chemical Research Institute
In order to help achieve the goal of “double carbon”, we have been working hard on “recyclable and usable”, and deeply ploughed into the field of polymer recycling.
In terms of “recyclable”, most of the packaging plastics on the market are multi-layer. These plastics are not only polyolefins, but different components add a lot of difficulties to recycling. To achieve “recyclable”, a very important step is to select a single raw material to produce plastic packaging, BOPE (biaxial tensile polyethylene) is a representative. This single material packaging structure is compared with the traditional packaging structure of multiple different materials, It is more conducive to the recycling of plastics.
In terms of “usable”, physical recovery and chemical recovery are the two main ways of recycling waste plastics. We always adhere to the principle of “walking on two legs” and develop a variety of technical routes to ensure that recycled materials can be used. In terms of physical recovery, we have cooperated with domestic well-known universities and enterprises to tackle key problems in the fields of continuous processing and reuse of recycled plastic film, secondary recovery technology of automobile plastics, and achieved initial results. In the field of chemical recovery, we have independently developed the microwave plasma pyrolysis technology, using waste polymer as the raw material for cracking, and the yield of triethylene is equivalent to the traditional naphtha steam cracking process. At the same time, we have accelerated the research and development work in the field of catalytic cracking, and focused on achieving efficient chemical recovery of various waste plastics. We have also developed a multi-phase solvent, which can be introduced into recycled plastics to improve the binding ability of various polymers, form materials with higher performance and stability, and is expected to realize the non-degradation reuse of hybrid plastics, which can be applied to household appliances, construction, transportation and other fields.
The recycling and reuse of waste polymer is an important part of the polymer industry in establishing and improving the green low-carbon circular development economic system. In the future, Beijing Institute of Chemical Technology will continue to focus on the development, application, recycling and recycling of new materials, work to improve the efficiency and quality of physical recycling, promote the research and development and industrialization of new chemical recycling technology, help build a new model of plastic recycling economy, and build a green economic closed-loop industrial chain.
Continuously develop green and environmentally friendly degradable materials
Li Renhai, director of safety production of Yizheng Chemical Fiber Company and head of research and development team of biodegradable materials project
At present, the development of biodegradable plastics still faces multiple challenges. Recently, the Research Report on Environmental Impact Assessment and Policy Support of Degradable Plastics, jointly researched by Sinopec and Tsinghua University, was officially released. Through detailed investigation and analysis, the research report proposed for the first time the evaluation index system of degradable plastics with degradability as the core compared with traditional plastics, and analyzed the feasible use path of degradable plastics from social and economic dimensions. We believe that this research report is a guiding opinion to lead the high-quality development of the biodegradable plastic industry. The research report puts forward the problems such as the structural contradictions in the use of biodegradable plastic products and the poor cost-effectiveness of using biodegradable plastic products in the field of general living sources.
Sinopec is the largest synthetic resin manufacturer in the world. It always advocates green development and attaches importance to the research, development and application of degradable plastics. It is the first member enterprise in Chinese Mainland. Yizheng Chemical Fiber continues to research and develop a series of green, environment-friendly, recyclable, recyclable and degradable polymer materials through joint research and production, strengthen technical research, improve production capacity, and strive to expand agricultural film and other markets, achieve higher quality and more efficient sustainable development, and continue to enhance the industrial influence of Sinopec’s biodegradable material element brand, “Ecorigin”, Further promote the leap of biodegradable materials from “product” to “standard” and from “product” to “brand”, and create a new green and clean business card of Sinopec.
Post time: Mar-08-2023





